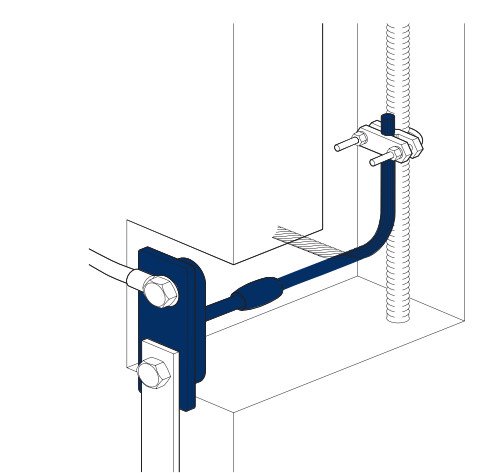
Earth Bonding Points With Exothermic Welding
Earth bonding points with exothermic welding refers to the process of creating electrical connections between different metallic structures on the Earth’s surface using exothermic welding techniques. These bonding points are crucial for ensuring a low-resistance path for fault currents and preventing the buildup of static electricity, thus enhancing the overall safety and efficiency of electrical systems.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Exothermic welding is a method of joining conductive materials, such as copper or aluminum, using a chemical reaction that produces intense heat and molten metal. In the context of earth bonding, this technique is employed to create robust connections between grounding electrodes, conductive grid systems, or other metallic components in contact with the Earth.
The process involves placing a powdered welding material in a graphite mold around the points to be bonded. An ignition source initiates the chemical reaction, resulting in a high-temperature molten metal that flows into the mold, creating a solid and durable connection. This fusion of metals ensures a low-resistance path for electrical currents, minimizing the risk of electrical faults and providing a reliable ground reference for various systems.
Earth bonding points with exothermic welding are widely used in applications such as telecommunications, power distribution, and industrial facilities where reliable grounding is essential. These connections contribute to the overall safety and stability of electrical systems by facilitating the dissipation of stray currents and minimizing the potential for electrical hazards.
- Earth bonding points are aviailable with pre- welded tails consisting of green/ yellow insulated earth cables with stranded copper conductors.