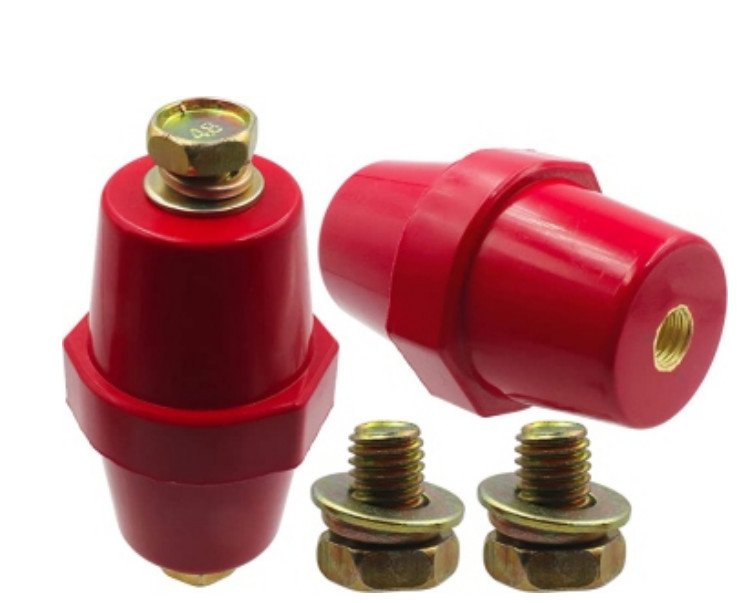
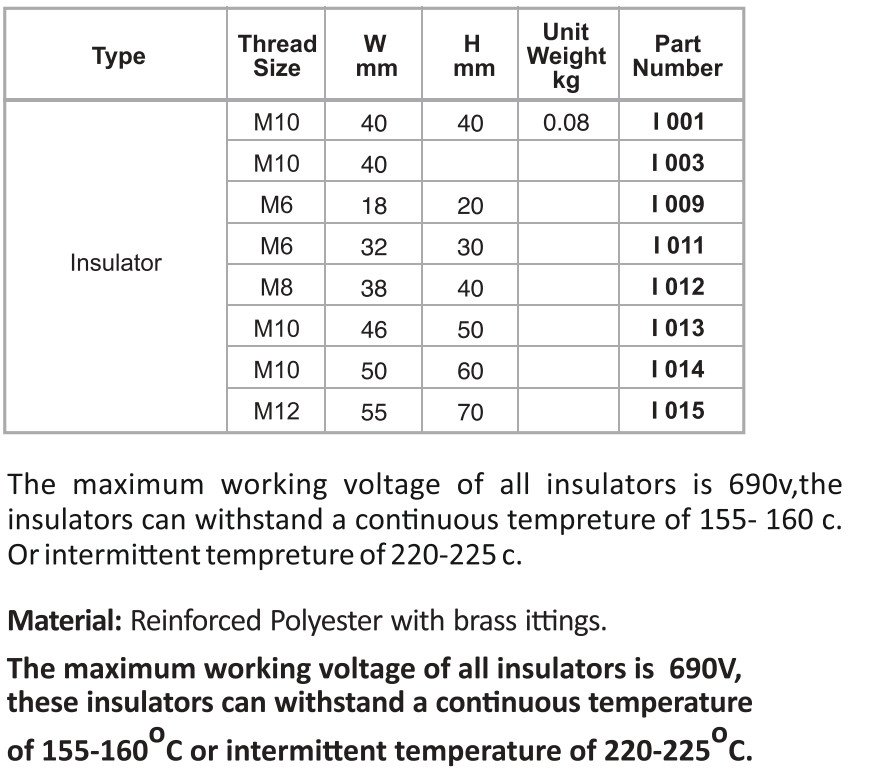
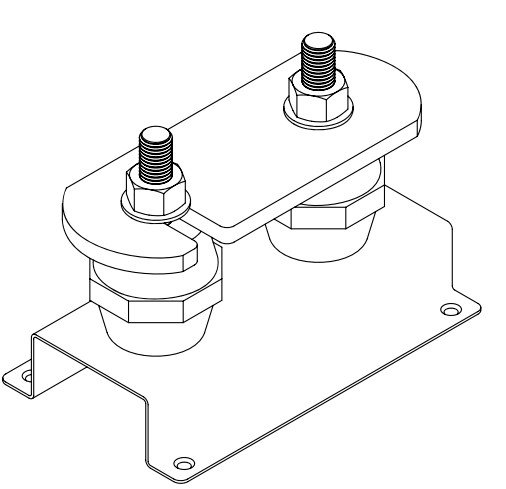
Insulators
Insulators are materials characterized by their high electrical resistance, which prevents the easy flow of electric current. They play a fundamental role in electrical and electronic systems by offering several key functions and benefits. Here’s a more detailed look at insulators:
Function and Importance
Preventing Electrical Leakage: Insulators are essential for preventing unwanted leakage of current. By surrounding conductive materials, they ensure that electrical current flows only through the designated paths, minimizing the risk of accidental electric shocks and equipment damage.
Ensuring Safety: In both residential and industrial settings, insulators are critical for safety. They protect individuals from electrical hazards by keeping live electrical components safely separated from grounded or non-conductive surfaces. This separation helps to prevent electric shocks and reduces the risk of fire caused by electrical faults.
Providing Electrical Isolation: Insulators create a barrier between conductive elements within electrical systems. This isolation prevents short circuits, which can occur if live wires touch each other or other conductive surfaces. It also ensures that different parts of an electrical system operate independently without interference from each other.
Enhancing System Efficiency: By preventing electrical leakage and minimizing energy loss, insulators contribute to the overall efficiency of electrical systems. They help maintain the desired electrical parameters and reduce waste, leading to better performance and lower operational costs.
Types of Insulators
Electrical Insulators: These are materials specifically designed to prevent the flow of electric current. Common examples include glass, porcelain, and various types of plastics. Electrical insulators are used in a wide range of applications, from household wiring to high-voltage transmission lines.
Thermal Insulators: While primarily designed to resist the transfer of heat rather than electricity, thermal insulators often also provide electrical insulation. Materials like fiberglass, foam, and certain ceramics are used to manage heat in electrical components and systems, reducing thermal stress and improving performance.
Mechanical Insulators: In some applications, insulators also provide mechanical protection, helping to support and protect electrical components from physical damage. For instance, insulator mounts and spacers can prevent physical contact between electrical components and support structures.
Applications
Power Transmission and Distribution: Insulators are used extensively in power transmission lines to support and separate electrical conductors from each other and from the supporting structures. They ensure that high-voltage lines do not make contact with towers, poles, or other conductive surfaces.
Electronics and Appliances: Inside electronic devices and household appliances, insulators prevent short circuits and electrical malfunctions. They are used in components like circuit boards, switches, and connectors to ensure reliable and safe operation.
High-Voltage Equipment: Insulators are critical in high-voltage equipment such as transformers and circuit breakers. They provide the necessary separation and protection to handle the intense electrical stresses present in these systems.
Cabling and Wiring: Insulated cables and wires are used in virtually all electrical systems, from residential wiring to industrial machinery. The insulation ensures that the electrical current flows through the conductors without leaking out or causing hazards.
Material Properties
High Electrical Resistance: Insulators have high electrical resistance, meaning they do not allow electric current to pass through easily. This property is crucial for ensuring that electrical energy is confined to its intended pathways.
Durability and Stability: Insulators must be durable and stable under various environmental conditions. They should resist degradation from exposure to moisture, heat, chemicals, and mechanical stress.
Dielectric Strength: This refers to the maximum voltage an insulating material can withstand without breaking down. High dielectric strength is essential for insulators used in high-voltage applications.
Insulators are indispensable in electrical and electronic systems, providing critical functions such as preventing electrical leakage, ensuring safety, and enhancing system efficiency. Their diverse applications and material properties make them essential for reliable and safe operation across a wide range of electrical and electronic environments.